System Classification Framework
System Classification Framework
A System Classification Framework provides a way to position a system-of-interest in a wider context of systems. This System Classification Framework is used to:
-
Identify types of systems.
-
Promote reuse across a set of systems and system types
-
Ensure alignment of similar types of systems and reduce duplicate definitions.
The System Classification Framework provides the following benefits:
-
A top level set of system types that can be used for any system-of-interest.
-
A way to reuse aspects of systems using generalizations that allow inheritance of the key elements of a system.
-
A way to integrate across systems based upon consistent references to defined systems using a single abstract system class..
-
A way to reuse AD Elements across the full set of defined systems (e.g. viewpoints, views, view components, other system descriptions, etc).
The top level System Classification Framework is based upon Peter Checkland's system classification model. Peter Checkland includes a system classification approach in his book Systems Thinking, System Practice. Peter Checkland's approach has been derived from Kenneth Boulding's original classification framework. The following form the top level set of systems in this classification scheme:
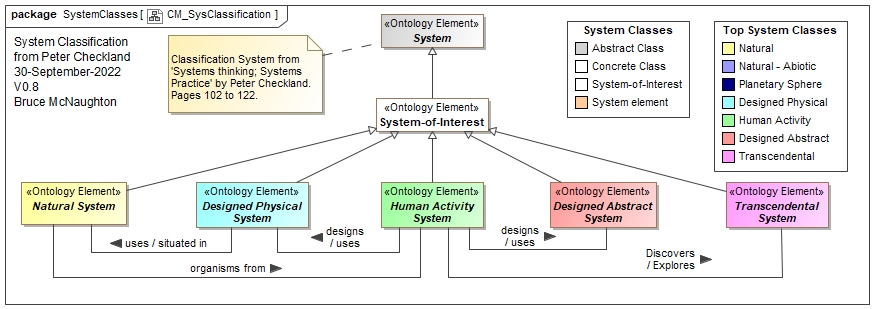
The top level System Classification Framework is described in the book from page 102 to page 122. Figure 4, page 112 highlights the 5 system classes. These classes are used as a top level classification for system types.
Link to the Top System Classifications PDF
Russell Ackoff's System Classification
Russell Ackoff's System Classifications were also considered. The following types of systems comes from Re-Creating the Corporation
- Deterministic System
- Animated System
- Social System
- Ecological System.
These classifications were considered; however, they use a "Purposeful System" as a differentiator between system types and was considered too narrow for this System Classification Framework.
Current Systems in the System Classification Framework
. The current systems that have been identified using the top level classification types are shown in the diagram below:
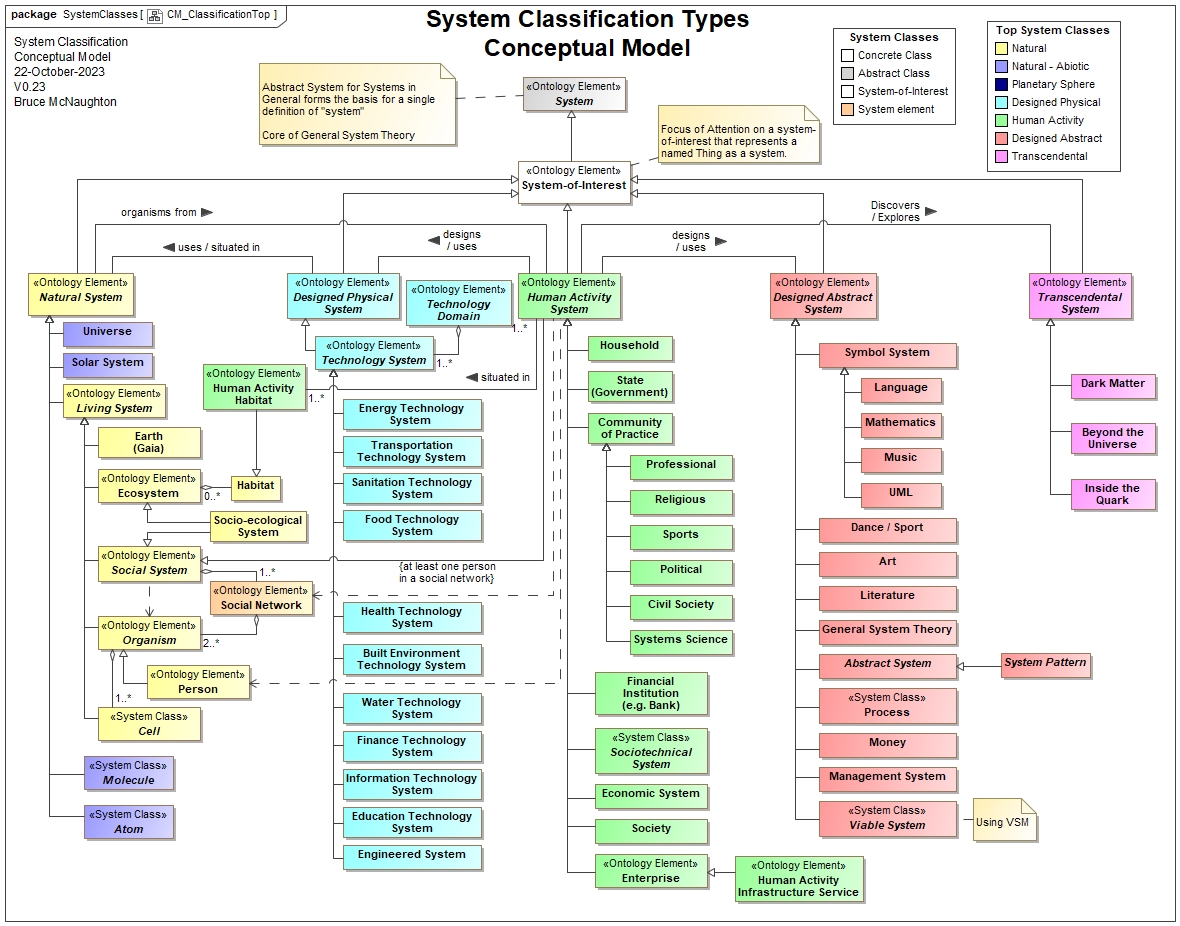
Note: that all of the types of systems are based upon a single definition and model of an abstract system. Each system inherits the single definition of system. This provides a consistent way to describe each type of system using a System Description based upon the SysDesc ADF.
System Classes
Given the consistent inheritance of a single definition of System (Abstract), any of the systems in the System Classification Framework can provide a generalization / inheritance path to retain the essence of the System Description (AD Element).
The identification of the above types of systems allows a consistent breakdown of systems. Here are some examples of further exploration of these systems: The system Breakdown Structure (equivalent to Figure 2 in ISO 15288:2015) is shown below:
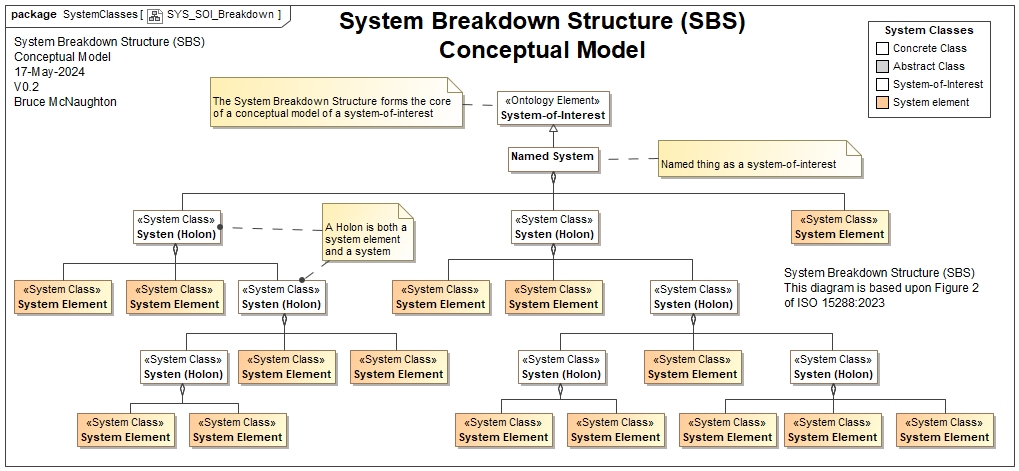
Each holon can be considered a system-of-interest and may have an associated System Description and / or System-of-Interest ADF. The top named system should be the primary candidate for the Architecture Description Framework. All holons can have a System Description. These holons can also be a mix of top level system types.
The Enterprise (SoS)System Description is a good example of multiple systems in a system description that mirrors the SBS.
PDF: System Description: Enterprise as a System of Systems (SoS),
Correspondences
In addition, the correspondences section of any System Description can also provide relationships between AD Elements where an AD element can also be a system Description. This allows correspondences across systems to be documented. This also allows for the sharing of system description AD Elements such as viewpoints, model kinds, correspondences or other AD Elements.