System Description: Society
Name: Society
Based on: Human Activity System (HAS)
Society: A society is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction, or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. Societies are characterized by patterns of relationships (social relations) between individuals who share a distinctive culture and institutions; a given society may be described as the sum total of such relationships among its constituent of members. In the social sciences, a larger society often exhibits stratification or dominance patterns in subgroups.
Societies construct patterns of behavior by deeming certain actions or concepts as acceptable or unacceptable. These patterns of behavior within a given society are known as societal norms. Societies, and their norms, undergo gradual and perpetual changes.
Nation: a large body of people united by common descent, history, culture, or language, inhabiting a particular country or territory
Citizen: Citizenship is a relationship between an individual and a state to which the individual owes allegiance and in turn is entitled to its protection.[1](quoted)
Each state determines the conditions under which it will recognize persons as its citizens, and the conditions under which that status will be withdrawn. Recognition by a state as a citizen generally carries with it recognition of civil, political, and social rights which are not afforded to non-citizens.
Legal System: included in society (To be added). Relate to deformation of character as laws and related to free speech. Includes rule of law.
Emigrant: a person who leaves their own country in order to settle permanently in another:
Refugee: a person who has been forced to leave their country in order to escape war, persecution, or natural disaster
Resident: a person who lives somewhere permanently or on a long-term basis (may or may not be a citizen but allowed to stay).
Indigenous peoples: are the holders of unique languages, knowledge systems and beliefs and possess invaluable knowledge of practices for the sustainable management of natural resources. They have a special relation to and use of their traditional land.
Migrant: a person who moves from one place to another, especially in order to find work or better living conditions
Nation-State: a sovereign state of which most of the citizens or subjects are united also by factors which define a nation, such as language or common descent.
Non-Violent action: Nonviolent action implies a commitment to utilizing nonviolent and creative means (e.g. acts of protest and persuasion, noncooperation, direct action, civil disobedience, boycotts, strikes, and education) to resist violent forces in order to influence and encourage social change.
Citizens' Assembly: A citizens' assembly (also known as citizens' jury or citizens' panel or people's jury or policy jury or citizens' initiative review or consensus conference or citizens' convention) is a body formed from randomly selected citizens to deliberate on important issues.
Democracy: a system of government by the whole population or all the eligible members of a state, typically through elected representatives:
Autocracy: a system of government by one person with absolute power
Kleptocracy: a society or system ruled by people who use their power to steal their country's resources:
Link to: System Description Society
The stated or implied purposes of the Society is to:
-
Provide a safe and just space for the members of the Society
-
Establish citizenship requirements for a set of people living in the society
-
Establish elections or other approach for selecting the leaders within the government.
-
Establish a tax mechanism to pay for the government of the society.
-
Participate in a global community and represent the needs of the citizens.
-
Establish shared values and beliefs for the society.
This section identifies the system properties. Suggested headings have been included. These can be tailored..
Systemic Measurable Variables
-
Ecological Stocks (natural capital)
-
Ecological Footprint
-
Basically the variables related to the doughnut of the society
Systemic Capabilities or Functions
-
Capabilities of the government based up the constitution and rule of law.
-
Governance mechanisms
-
Economies (markets and commons)
-
Capabilities of the citizens (vote, pay taxes, etc).
System States
-
Developing
-
Ongoing
-
Thriving
-
Failed
Systemic Quality Properties
-
Wellbeing and Health of the members of the Society
-
Coherence of the messages between the leaders and the citizens (degree of Truth).
-
Coherence and equality of the application of the rule of law.
-
Inclusive participation of all members of society.
System Quantity Properties
-
Population of the society (by type of member if available)
-
Size of ecosystem(s) or territory of the society.
The stakeholders of the society fall into a number of different typestypes:
-
Members of the Society
-
Citizens
-
Residents
-
Emigrants
-
Migrants
-
Refugees
-
Indigenous people
-
-
Stakeholders outside of the Society
-
Members of other societies
-
who want to emigrate or migrate
-
who are citizens but residents of other countries
-
-
-
Organizations or institutions inside the Society
-
Any human activity system (see types).
-
-
Organizations or institutions outside the Society
-
Other Societies
-
United Nations
-
This area also includes the stakeholders that are unable to represent their needs.
-
Organisms living within the society (trees, animals, plants, etc).
-
Organisms living outside the society (trees, animals, plants, etc) that are impacted by the society-of-interest.
The environment is the systems that are outside of the society. The society consists of all of the human activity systems situated in the society ecosystem. The society also contains all of the organisms (non-human) living in the ecosystems of the society.
The environment and the potential impacts on the system-of-interest.
This includes the effects of other societies on the climate, any of the spheres, etc.
The Environment also consists of the mechanisms of trading between societies. These trading arrangement provide for ways to pay for imported items. The trade also has some potential drawbacks by exploiting resources of one society at the expense of another. This may lead to dependencies on external sources of supply.
this section includes
- Transactional
- Contextual
- Regulatory
Identification and Composition of System elements and their relationships. This section generally includes a system conceptual model.
System Element: Identification and Relationships
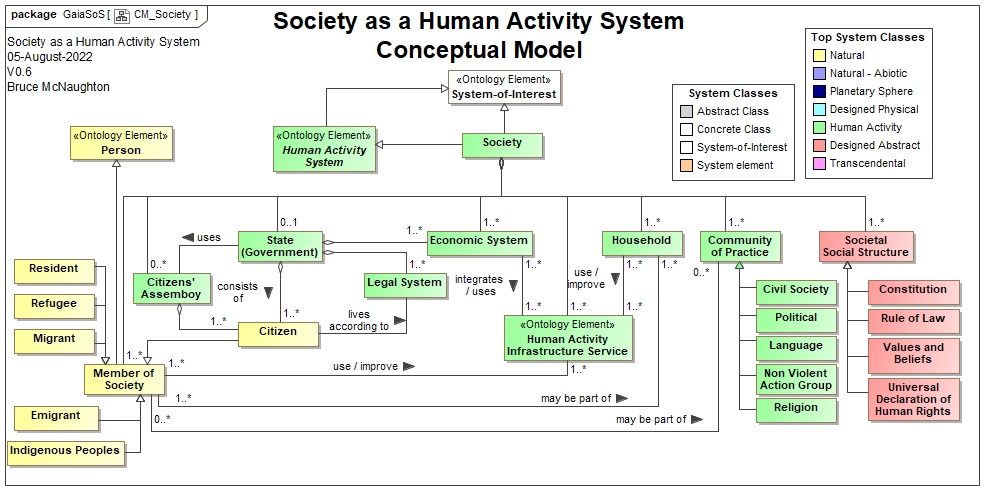
The above diagram shows the various types of members of society and the various human activity systems that are part of the society.
In addition to the human activity systems, there is the social structure that provides the shared understanding of the society. This is generally a constitution or rule of law. This social structure also provides the basis for the shared values and beliefs of the society. These are critical for creating a well defined society.
In addition, the culture for the society is based upon the social structure and the network of communication formed by the members. The social interactions may be through face to face, some written information using the appropriate language and symbol systems and the use of social media (internet based communication).
In some cases, the social media (social technology) may amplify false messages to distort the truth, or through AI algorithms, impact personal decisions through playing on cognitive biases of people.
Describes a specific instance (configuration of components) of a system structure and this systems behaviour.
Describe the response of the system due to various triggers
Configuration / Scenario:
Specific Configuration of society
NOTE: The structure (pattern of organization) provides a conceptual model of may types of societies. Once the type of governance structure and people have been selected. The behaviour of the specific system can be established. The current descriptions are for a democratic society. Autocratic or Kleptocratic societies will have different processes and behaviour.
Cyclical (Repeating / Regular) Processes
Routine operational processes to maintain the system
Provides support to deliver the capabilities or functions of the system.
Trigger: Time for elections Process: Election process as specified in the constitution
Trigger: Time to set budget and collect taxes; Process Budget and tax collection processes
Trigger: maintain infrastructure Process: maintain human activity infrastructure elements for future generations use.
Trigger violation of the rule of law Process: initiate legal processes
Trigger: Initiate annual planning Process carry out budgeting and planning processes.
Trigger: Initiate cultural event Process conduct the cultural event.
Trigger: Initiate Citizens' Assembly to explore topic Process: Conduct Citizens' Assembly to gain feedback on a topic or topics.
Development Life Cycle Processes
How this system is created, developed, used and released.
Describes the processes for major developmental changes.
John Grubb
Age of Pioneers
Age of Conquest
Age of Commerce
Age of Affluence
The Age of Intellect
The Age of Decadence
Collapse
Religion
Joseph Tainter
Collapse of societies (to be added)
Other developmental processes
Technology innovation
Social innovation
Governmental innovation
Non violent action groups (to initiate structural changes)
More to be added in this section over time.
Key issue surfacing is the legal system or justice system and how to remain independent and not political.
The following references support this type of system-of-interest.