Name: Organization
Based on: Human Activity System (HAS)
A "Team" (typically temporary) and "Org Unit" (typically permanent) are organization types. "Org Unit" and "Team" typically consist of a manager and members (a single bounded unit).
The organization is defined as:
ISO 9000:2015: organization: person or group of people that has its own functions with responsibilities, authorities and relationships to achieve its objectives.
PDF: System Description: Organization as a SoS,
The Organization is a fractal concept. The term organization can represent:
- The Whole Organization comprising many smaller organizations
- A single element of the organization structure
In the book, The Puritan Gift, by Kenneth and William Hopper, they have identified 25 underlying principles of good management practice. Principle 1 is the following:
- "All successful organizations, however simple, consist of systems within a system."
In this way, the Organization as a whole is a system and so are each of the teams within the Organization.
An organization can take on an organizational role within an Enterprise Value System. These are:
The value system consists of all of the supplier, customer, channel and central organizations that deliver value to customers.
Within an organization, there may be many types of organizations. The following diagram shows some of the types of organizations within an organization.
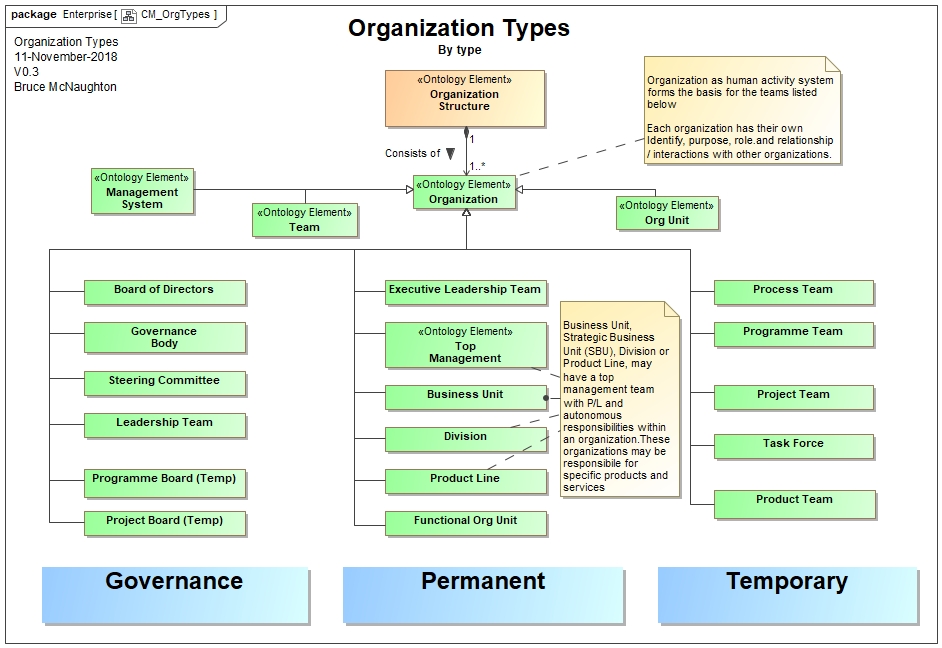
Note that any of these types may consist of additional organizations as system elements.
“The purpose of an organization is to enable ordinary human beings to do extraordinary things.” Peter Drucker
The Organization exists to achieve its purpose and role as part of the Enterprise (SoS).
The plans and objectives of the organization provide the context for establishing both current and future capabilities needed to achieve these objectives.
The purpose and objectives are aligned to the strategic plan of the enterprise.
The organization is one of the dimensions of the 3D Operating Model.
Systemic Measurable Variables
The emergent properties of the whole Organization can be seen in two ways
Planned and managed:
- Achieve performance objectives and targets
Expected and desired
- High customer satisfaction and continued use
- Positive and motivating culture within the organization
- Positive contribution to society and the economy
Systemic Capabilities or Functions
The Organization delivers the following functions or capabilities:
- Establish and realize the capabilities to achieve the purpose of the Enterprise as a System of Systems (SoS)
- Deliver the products and services of the organization
- Easily adapt to changes in the environment
- Development of suppliers capabilities to enable the organization to meet its objectives.
The way the organization senses and responds to any of the emergent properties leading to undesired properties can determine the long term sustainability of the organization.
System States
The top management team establishes the state of the organization.
- Architectural states
- Identified: The name of the organization is identified
- Defined: The capabilities needed to achieve the purpose and objectives are defined. The Enterprise (SoS) Architecture Description or the Operating Model describes the architecture of an organization.
- Transformational States
- Manager Appointed: A manager has been appointed.
- Planned: The plan prepared to establish and implement the capabilities is approved.
- Operational States
- Active: The Organization is now operational. All other systems are created, managed and released. The operating model now describes the current state of the organization.
- Closing: The top management team has decided to close the organization.
- Closed: The organization is closed and the Enterprise as a System of Systems (SoS) may cease to exist.
The current state is the current active organization and its current Operating Model. The target or future state is the state described by the Target Architecture Description (or the Target Operating Model). There may be any number of intermediate states that move this organization forward towards the target state.
These states are changed through the change and transformation capabilities as described in the life cycle sections below.
Stakeholders and their Concerns
Managers (all levels)
- Will this organization achieve its purpose and objectives?
- Is the organization sustainable for the long term?
- Are our customers satisfied?
Employees / Contractors
- Will my contribution help the organization be successful?
Customers
- Will my needs be met?
Suppliers
- Do we have a win / win relationship?
An organization takes an organizational role in the Enterprise as a System of Systems (SoS). This role determines the contribution to the enterprise objectives as a whole. The Organization is a system element (constituent system) of the Enterprise as a System of Systems (SoS). The Enterprise provides part of the environment for the organization. This is shown in the following picture:
The environment includes the following items that can impact the capabilities and performance of the Organization:
- Competition
- Government
- Physical Environment
- Local communities
- Transportation
- etc.
The Structure of the Organization as a system is described below:
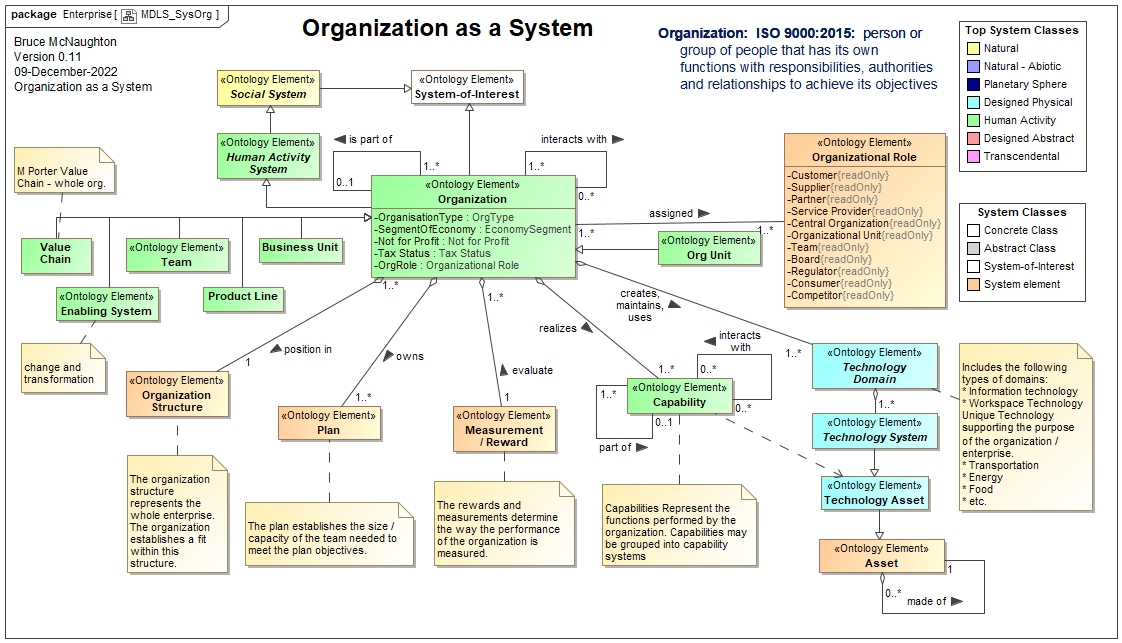
The relationships between these system elements can be seen in the manager friendly team model. An alternative picture of the team system element interactions is shown below:

This picture is an adaptation of the STAR Model identified by Jay Galbraith in his 1977 book, Organization Design. This model is a fractal model that applies to an individual team or the whole organization. This model is also used as the basis of an Operating Model that can be used at any level within the organization.
The Organization consists of a number of system elements. These system elements are:
Configuration / Scenario:
Describes any configuration / scenario attributes for a specific system-of-interest. This may not be appropriate for all system descriptions (e.g. patterns or abstract systems).
Cyclical (Repeating / Regular) Processes
The organization is created, used, or released in an organization using the Team Performance Management using the organizing Activities of a Manager. Additional capabilities create the environment for the organization as a whole to deliver its purpose. The Top Management Team manages the creation, use and release of the whole organization rather than a specific team..
Development Life Cycle Processes
The organization as a whole creates, uses and releases any of the capabilities necessary to design, change or enhance the capabilities of the organization. This set of change capabilities forms the Enabling Systems necessary to create the operational capabilities for the normal operations of the organization. Feedback from the performance of the organization is used to make both minor and major changes to the organizations. The overall investment and priorities of the organization guide the portfolio of change and the roadmap. See Enabling System
The following references support this type of system-of-interest.
Book References
Adaptive Enterprise, Stephan Haeckel
Competitive Advantage, Michael E. Porter
Management: Tasks, Responsibilities and Practices, Peter Drucker
Organizational Culture and Leadership, Edgar H. Schein
Leading Organization Design, Gregory Kesler and Amy Kates
Managing Corporate Lifecycles, Ichak Adizes, Ph.D.
The Puritan Gift, Kenneth Hopper and William Hopper
Competing by Design, David A. Nadler and Michael L. Tushman
Concerns